CHALLENGE
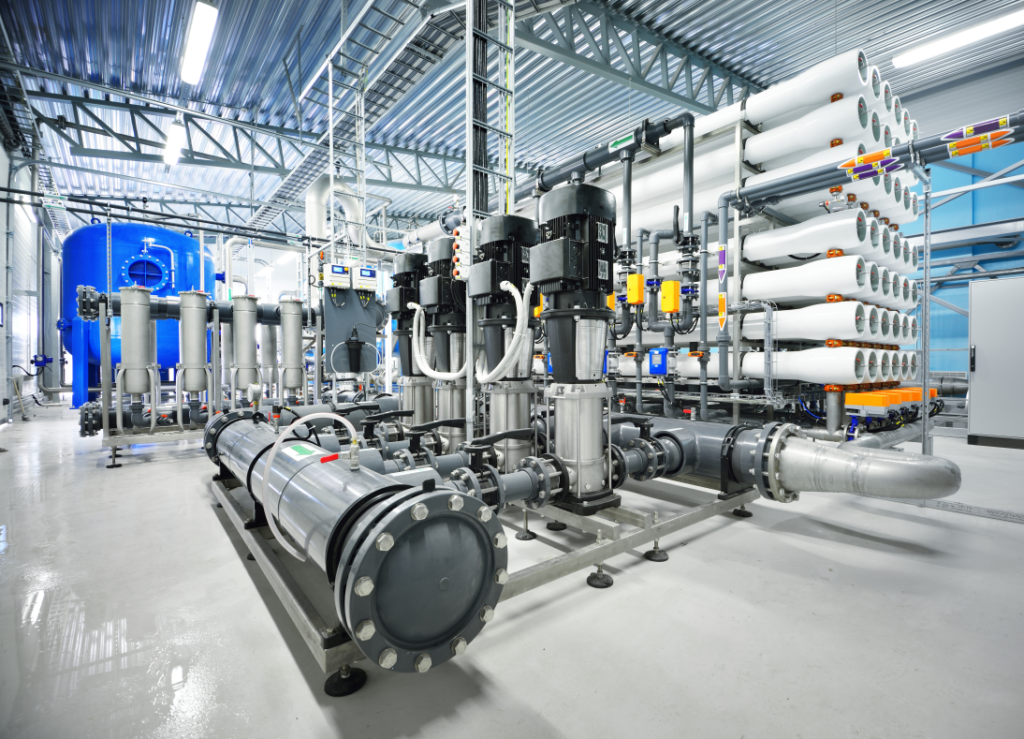
The client was looking for a more efficient and safer alternative to replace the formulated citric acid used in the cleaning of reverse osmosis membranes.
SOLUTION
Samples of Enviro-Syn® HCR-IND were tested and compared with the formulated citric acid (CA-1) to clean a polyamide reverse osmosis (RO) membrane fouled with calcium deposits. Enviro-Syn® HCR-IND was used at a 2% dilution with deionized water to test the strongest acid concentration to which the membrane would be exposed. The results of Enviro-Syn® HCR-IND were compared with a 1% dilution of the CA-1 cleaner to evaluate membrane compatibility.
All coupons were cleaned for three hours with alternating periods of circulation, soaking, and circulation.
The flow was measured at 10.6 psi and corrected to 68°F (20°C), using an NaCl solution with 2000 ppm of total dissolved solids.
RESULTS
The results of the flow and salt rejection tests are shown in Tables 1 and 2 below. The tests resulted in a final flow 14% higher with Enviro-Syn® HCR-IND compared to CA-1, achieving similar final salt rejection results.
Table 1: Flow Change in Fouled Coupon
| Flow (L/day·m²) | Final Flow (L/day·m²) | % Increase | |
| Enviro-Syn® HCR-IND | 89 | 440,1 | 394 |
| CA-1 | 244,5 | 387,1 | 58,3 |
Table 2: Salt Rejection in Fouled Coupon
| Initial Salt Rejection (% | Final Salt Rejection (%) | |
| Enviro-Syn® HCR-IND | 85 | 96 |
| CA-1 | 92 | 95 |
These test results indicate that Enviro-Syn® HCR-IND is a viable substitute for citric acid in reverse osmosis cleaning formulations and did not cause damage to the membrane. In addition, it provided significant occupational health benefits by greatly reducing the risk of injury during the cleaning operation and minimizing equipment corrosion. In the next cleaning procedure, a 1% concentration of Enviro-Syn® HCR-IND will be used.